Lectures and readings are often seen as the staples of any modern education, but are they necessarily the best approach for getting students to develop the hands-on skills necessary for a counselling career? While lectures do have their merit, many experts believe that experiential learning, also known as learning by doing, is the most effective option for promoting true understanding.
There are many reasons why experiential learning is essential for students completing a professional counsellor diploma. Great counsellors need to be confident in their practical skills and go beyond theory and textbook knowledge. The ability to connect with clients, ask the right questions, and provide guidance can only arise from developing real competency through a hands-on education. This is why the best professional counsellor training programs will place a heavy emphasis on experiential learning, as they prepare students to make a smooth transition into their careers after graduation.
Do you want to learn more about the value of experiential learning? Here’s a look at the benefits of this approach.
The Value of Experiential Learning
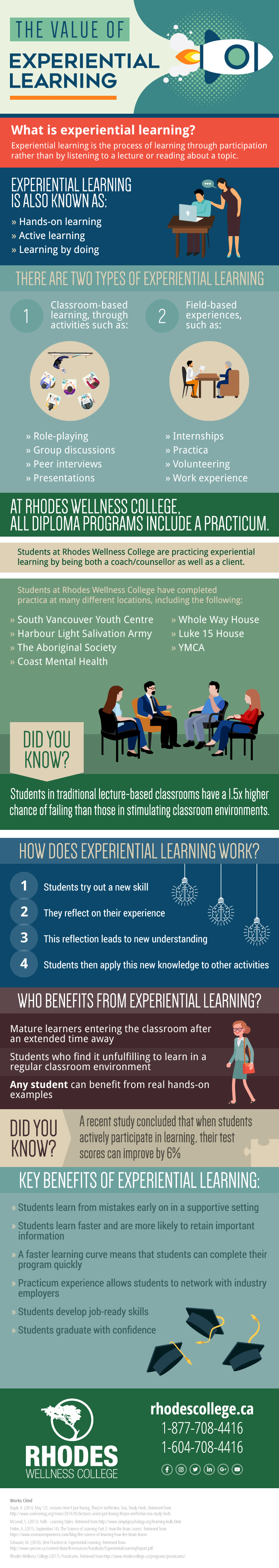
What is experiential learning?
Experiential learning is the process of learning through participation rather than by listening to a lecture or reading about a topic.
Experiential learning is also known as:
Hands-on learning
Active learning
Learning by doing
There are two types of experiential learning
- Classroom-based learning, through activities such as:
- Role-playing
- Group discussions
- Peer interviews
- Presentations
- Field-based experiences, such as:
- Internships
- Practicums
- Volunteering
- Work experience
At Rhodes Wellness College, all diploma programs include a practicum.
Students at Rhodes Wellness College have completed practicums at many different locations, including the following:
- South Vancouver youth centre
- Harbour Light Salivation Army
- Coast Mental Health
- Whole Way House
- The Aboriginal Society
- YMCA
- Luke 15 House
Did you know?
Students in traditional lecture-based classrooms have a 1.5x higher chance of failing than those in stimulating classroom environments.
How Does Experiential Learning Work?
- Students try out a new skill
- They reflect on their experience
- This reflection leads to new understanding
- Students then apply this new knowledge to other activities
Who benefits from experiential learning?
Mature learners entering the classroom after an extended time away
Students who find it unfulfilling to learn in a regular classroom environment
Any student can benefit from real hands-on examples
Did you know?
A recent study concluded that when students actively participate in learning, their test scores can improve by 6%
Key benefits of experiential learning:
- Students learn from mistakes early on in a supportive setting
- Students learn faster and are more likely to retain important information
- A faster learning curve means that students can complete their program quickly
- Practicum experience allows students to network with industry employers
- Students develop job-ready skills
- Students graduate with confidence
Works Cited
Bajak, A. (2014, May 12). Lectures Aren’t Just Boring, They’re Ineffective, Too, Study Finds. Retrieved from http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2014/05/lectures-arent-just-boring-theyre-ineffective-too-study-finds
McLeod, S. (2013). Kolb – Learning Styles. Retrieved from http://www.simplypsychology.org/learning-kolb.html
Potter, A. (2015, September 14). The Science of Learning Part 2: How the Brain Learns. Retrieved from https://www.envisionexperience.com/blog/the-science-of-learning-how-the-brain-learns
Schwartz, M. (2010). Best Practices in Experiential Learning. Retrieved from http://www.ryerson.ca/content/dam/lt/resources/handouts/ExperientialLearningReport.pdf
Rhodes Wellness College (2017). Practicums. Retrieved from https://www.rhodescollege.ca/programs/practicums/